Drinking water disinfection
The disinfection of drinking water is necessary because along the pipes, it is always possible to conceal some colony of bacteria (legionella and other) that endangers its potability.
Using the ECA technology in continuous dosing, it is possible to guarantee complete disinfection of the water.
The dosages involved are extremely low and depend on the length of the pipes to be treated, the presence of biofilm, the level of contamination, etc.
In general, the normal dosage varies from 0.1% (0.5ppm) to 0.5% (2.5ppm) which allows to guarantee an active chlorine level in the pipes of 0.2ppm in accordance with the main regulations in force.
Below is a typical installation example:
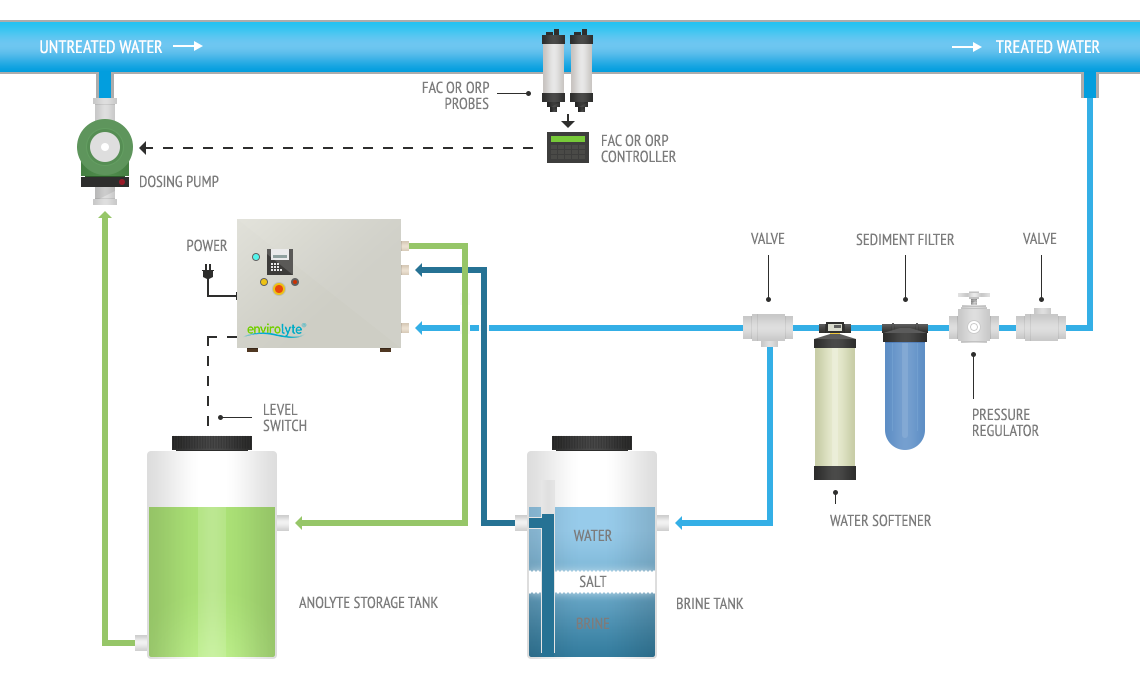
As you can see, the system is quite simple: the ECA unit is fed directly from the aqueduct water and uses the brine that is caught from a tank in which the kitchen salt is dissolved.
The tank allows to obtain the maximum degree of salt saturation which is 28%.
The unit generates the ORPICYL, which is stored in a tank, a dosing pump picks it up to feed it into the main duct and keeps the level constant by adjusting the dosing by means of the information sent to it either from a meter launches pulses, or from a redox probe, or from a probe for the measurement of chlorine. The choice of instrument depends on the needs of the system.
Below are some installations in the world:
Using the ECA technology in continuous dosing, it is possible to guarantee complete disinfection of the water.
The dosages involved are extremely low and depend on the length of the pipes to be treated, the presence of biofilm, the level of contamination, etc.
In general, the normal dosage varies from 0.1% (0.5ppm) to 0.5% (2.5ppm) which allows to guarantee an active chlorine level in the pipes of 0.2ppm in accordance with the main regulations in force.
Below is a typical installation example:

As you can see, the system is quite simple: the ECA unit is fed directly from the aqueduct water and uses the brine that is caught from a tank in which the kitchen salt is dissolved.
The tank allows to obtain the maximum degree of salt saturation which is 28%.
The unit generates the ORPICYL, which is stored in a tank, a dosing pump picks it up to feed it into the main duct and keeps the level constant by adjusting the dosing by means of the information sent to it either from a meter launches pulses, or from a redox probe, or from a probe for the measurement of chlorine. The choice of instrument depends on the needs of the system.
What are the benefits of this disinfection?
- - Given the low concentration of active chlorine, the diluted ORPICYL in the water does not cause any toxic effect or form any toxic by-product;
- - ORPICYL penetrates small pores of water pipes and any other material;
- - ORPICYL eliminates biofilm and algae from the distribution system;
- - Water pipes and equipment should not be rinsed with water after disinfection;
- - ORPICYL eliminates the taste and smell of chlorine;
- - Improves flavour and eliminates the smell of algae;
- - L' ORPICYL, if properly stored, maintains its characteristics up to 6 months from the date of production;
- - Has a high ease of dosing;
- - Ha un elevato livello di sicurezza data l'assenza di sostanze chimiche pericolose utilizzate o prodotte.
Why is ECA technology better than traditional chlorination?
- -Although apparently similar to chlorine, ORPICYL is unique in its kind and is superior to sodium hypochlorite in the destruction of spores, bacteria, viruses and other pathogenic organisms. Sodium hypochlorite in a concentration of 5% is only effective in disinfection, but not in sterilization. Sodium hypochlorite is not effective against cysts (Guardia, Cryptosporidium);
- - Most pathogens, develops resistance to sodium hypochlorite over time. The application of ORPICYL, as a daily water disinfectant on a daily basis for more than ten years, has shown that microorganisms do not develop resistance to ORPICYL over time;
- - The contact time required for the ORPICYL is lower;
- - Sodium hypochlorite loses its activity during long-term storage and poses a potential hazard of gaseous chlorine emission during storage;
- - The reaction of ORPICYL and organic materials produces about half of trihalomethanes compared to chlorine;
- - The biofilm in the pipes is eliminated.
Below are some installations in the world:



